Batteries? What For?
Have you ever been curious about the multitude of battery types and functions? Let's take a look at a few with guest author Andrew Shepherd.
This is a guest blog post from Andrew Shepherd. Andrew has been studying electronics in earnest for over a decade and loves working with his mind and hands. He specializes in analog electronics, but his interests are eclectic and span seemingly unrelated areas.
If you need a project to be portable, here’s a small crash course on some of the batteries that are available and what situations they are good for.
Types:
There are two main types of batteries: primary and secondary – batteries that can be recharged and those that are one-use-only. Today we'll cover only the most relevant and available types for the sake of brevity, as the full catalog of battery types could fill pages. We will also only explore certain secondary batteries.
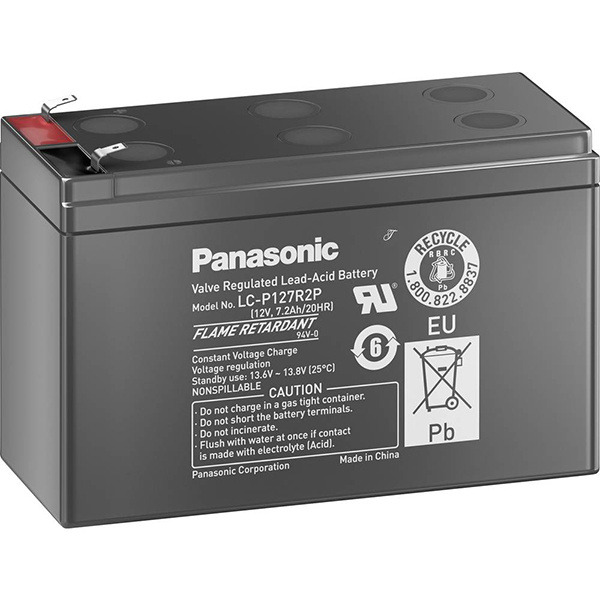
Lead-Acid - This is the oldest type of rechargeable battery. They can supply a lot of current but are also very heavy compared to newer types. They tend to be used in cars and stationary equipment, like UPSs (Uninterruptible Power Supplies), due to their durability and tolerance for low temperatures. Cell voltage is ~2.1 V each, but they typically come in 6V or 12V packs. Charging and discharging is quite simple, as long as the upper and lower voltage bounds are not grossly exceeded and the charge current is not too high. If they are abused they can outgas hydrogen and potentially explode.

NiMH - These are an improvement on the NiCd batteries, and are a proven and reliable battery technology. They are more power dense than lead-acids, but have a lower cell voltage of ~1.2V under load. Recharging and discharging is also fairly simple given that you don’t draw current below a certain voltage. If abused they can overheat and lose a lot of their capacity.
2500 mAh NiMH Battery - AA
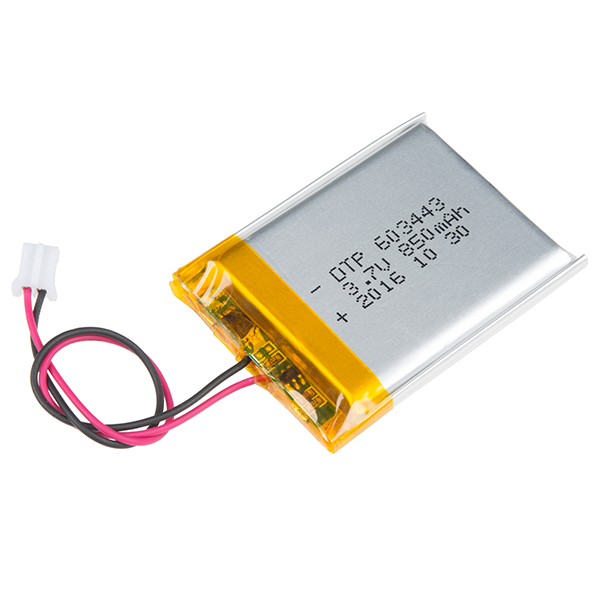
PRT-00335LiPo/Li-Ion - The difference between LiPo and Li-Ion is subtle and the technologies are typically combined for most batteries, so they will be regarded together. These are lightweight, high power density, high cell voltage (3.7V under load). Their output current capability is consistently better than NiMH for a given size. Their disadvantage is they are less stable than other batteries and care must be taken when charging or discharging. The charging process is more complicated and requires a special process to avoid damage. For multi-cell systems, cell balancing is required for charging and discharging. If these batteries are abused, they can explode and shoot flames and fluoride gas everywhere.
Types of LiPos
These things come in all shapes and sizes and can be used for many applications due to their high power density.
Small Li-Ion Flat Packs - These are useful for small projects and most can interface directly with many SparkFun products. Paper-thin, flexible batteries also exist and may be best for wearables.
18650s - Shaped like a large AA battery, these are a versatile store-and-replace cell with lots of current capability and capacity. Their main advantage is they can be swapped in and out, or be bundled together into a pack.
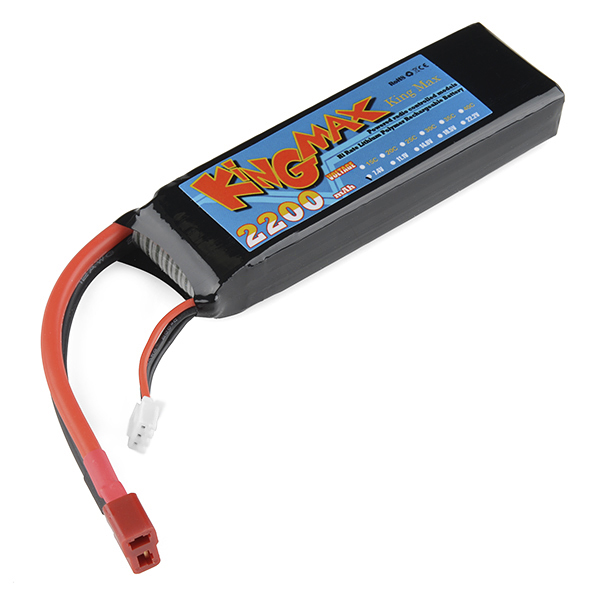
Multicell Packs - If you need more voltage than 3.7V this is the way to go. You’ll need a charger capable of cell balancing to use them, however.
Lithium Ion Battery - 2200mAh 7.4v
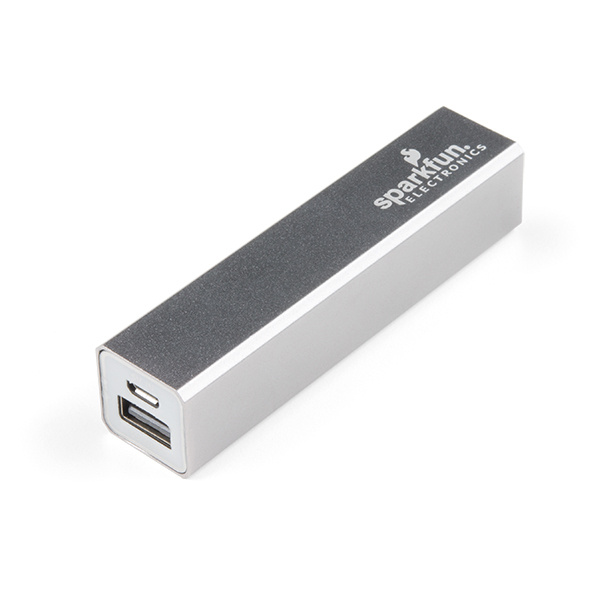
PRT-11856USB LiPo Pack - These are useful for small Arduino projects because they provide USB power (5V at 1A) in a small, handy package.
Lithium Ion Battery Pack - 2.5Ah (USB)
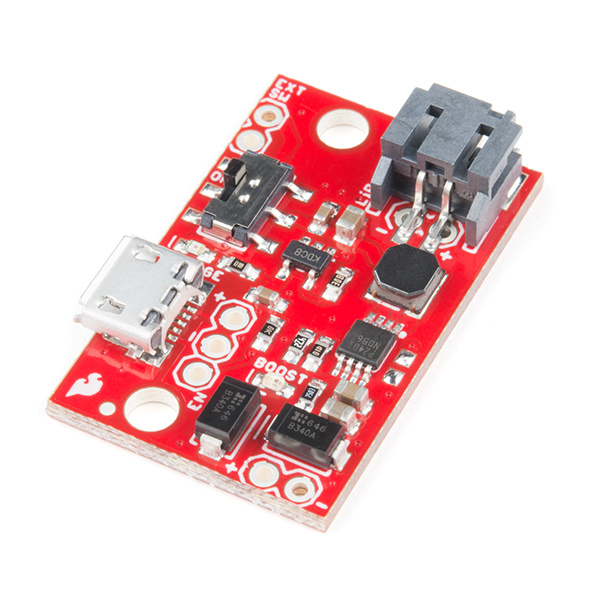
PRT-14367LiPo Management
USB Chargers - This USB LiPoly Charger runs from either a DC jack or a micro USB connection and charges a single cell Li-Po through a common JST connector. It also has an output port so it can be used in a project without reconnecting the battery after charging. This charger lets you adjust how much current you want to charge with a basic USB charger.
Boost Converter - This takes a single cell 3.8V LiPo and boosts the voltage up to 5V to make it usable for most microcontroller and LED circuits. It can source up to 1A of current.
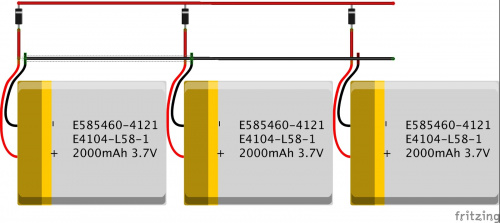
Multiple Cells
What if you need more voltage or current capability? The solution is to add cells in series for more voltage, and cells in parallel for increased current capability and capacity. With LiPos especially, it is critical the cells can charge and discharge correctly. You can put cells in parallel with each other, but they must be protected somehow. Otherwise, they can discharge into each other and cause damage. One way is to use a Schottky diode in series with each cell, which will allow current to pass out of each cell but prevent damage if one cell gets lower than the others.
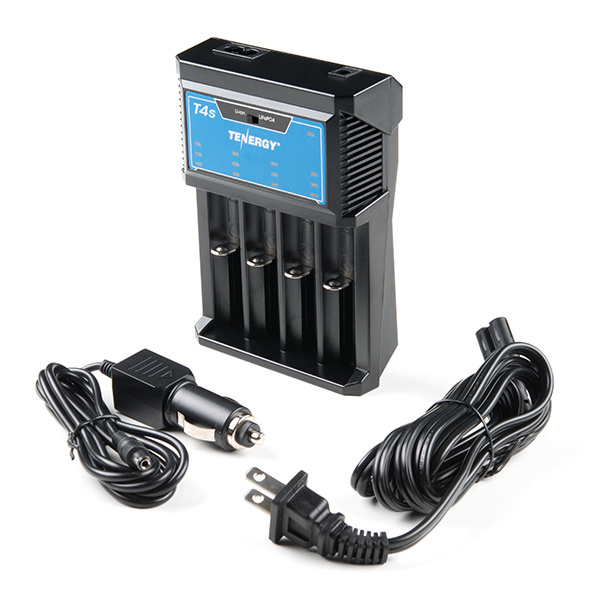
Charging multiple cells requires cell balancing or separate chargers for each cell. The advantage of 18650s is that they can be removed and charged separately in a bay like this.
Useful Resources and Further Learning
- Dave Jones of EEVBlog explains the charging process of LiPos. It lends clues as to why the charging process is more complicated than NiMH or other batteries, and discusses how you could make a charger yourself.
- This website carries a lot of different types of batteries, including special ones that might be hard to find elsewhere.
- DIY battery charger using the TP4056 chip.