Precision Meets Customization Meets...You! Meet the MicroMod GNSS Carrier Board!
A look into the MicroMod GNSS Carrier Board and how to utilize it with u-center.
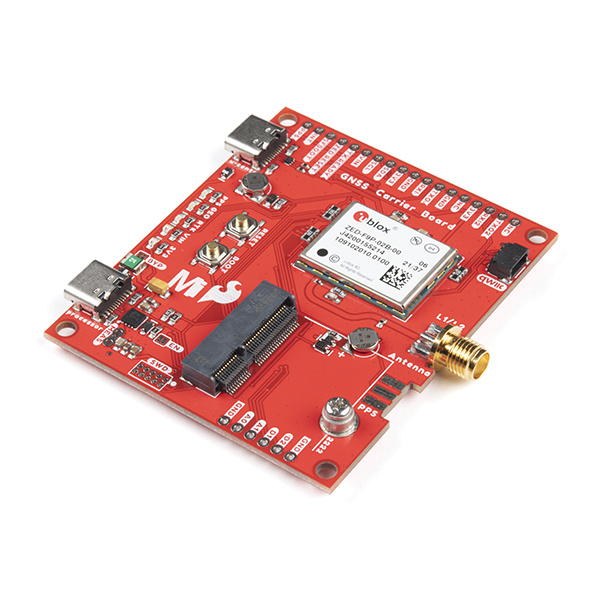
As you can probably tell with the last few product releases, we're really excited about all things geospatial. One of our larger recent product releases, the new SparkFun MicroMod GNSS Carrier Board, exemplifies everything that is so revolutionary in that space right now. This board, equipped with the ZED-F9P chip from u-blox, sits at the convergence of highly-precise and highly-configurable. Plus, being a MicroMod board, it is part of a highly-customizable ecosystem that makes it easy to utilize different processors depending on your specific project needs.
Overview of the board
The ZED-F9P chip on the SparkFun MicroMod GNSS Carrier Board is a top-of-the-line module for high accuracy GNSS and GPS location solutions, including RTK, capable of 10mm, three-dimensional accuracy. With this board you will be able to know where your (or any object's) X, Y, and Z location is, roughly within the width of your fingernail! The ZED-F9P is unique in that it is capable of both rover and base station operations. Utilizing the M.2 and Qwiic connectors, no soldering is required to connect it to the rest of your system. However, we still broke out 0.1"-spaced pins in case you prefer to use a breadboard to attach additional peripherals.
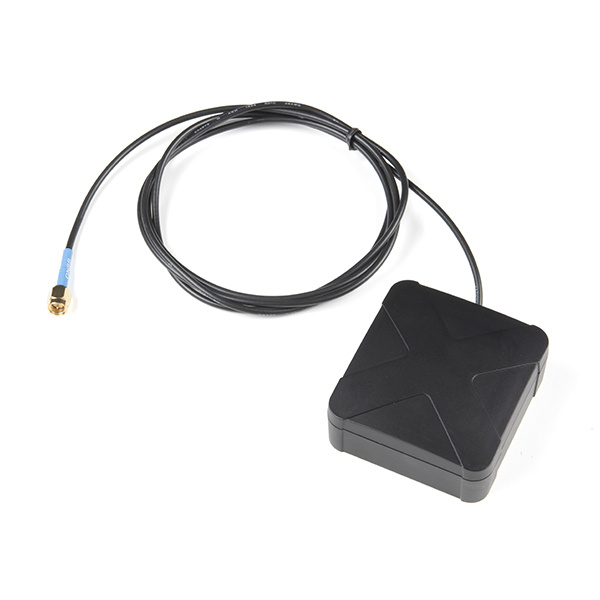
To properly utilize this kind of module, you'll want to use an antenna that can get a clear view of the sky. It will need to be one that is robust enough to be outside, has long cable, and has an SMA connector.
The Taoglas AA.200 MagmaX2 Multiband GNSS Magnetic Mount Antenna is a good choice for the job. It can access most major constellations including GPS (L1/L2/L5), GLONASS (G1/G2/G5), Galileo(E1/E5a/E5b) and BeiDou(B1/B2). The AA.200 antenna is an active multiband GNSS magnetic mount antenna that exhibits excellent gain and good radiation pattern stability. The combination of these elements help ensure the best possible positional accuracy for systems where RTK is enabled and disabled.
Lastly, you'll need to pick up a processor board of your choosing; you can use our comparison chart to decide, or try a few out!
SparkFun MicroMod RP2040 Processor
DEV-17720SparkFun MicroMod STM32 Processor
DEV-17713As usual, we produced a product showcase that goes through the board specs and capabilities in depth. We also included a more complete understanding of the many different GNSS technologies that the ZED-F9P chip utilizes, as well as different software platforms to make full use of the module.
How to configure using u-center
For any board based on u-blox chip, using u-center, a Windows free software tool, is an easy way to configure your receiver. We have a robust beginner tutorial on connecting your receiver with u-center through configuring your COM port and baudrates. Make sure that your antenna has a clear view of the sky, and once you're connected you'll see a breadth of data appear.
Start by configuring your hardware:
Seeing your satellite connections
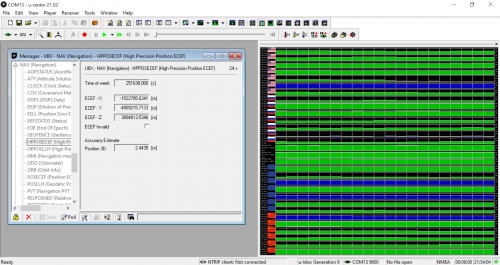
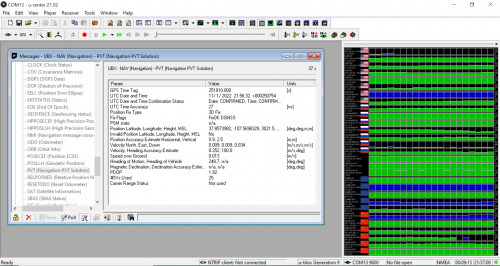
There are two things to note in the next screenshot - firstly, that the receiver is acquiring data from multinational satellite constellations, meaning it is a proper GNSS tool. You can see on the right hand side that is communicating with GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou satellites. You can also see, in the second screenshot, that the module sis communicating with 25 satellite units at the moment, so it is gathering a lot of information. The other thing to note, is that without any correction data, the module is within 2 meters of accuracy. We have a tutorial on using NTRIP to stream correction data to your device using both u-center and other platforms.
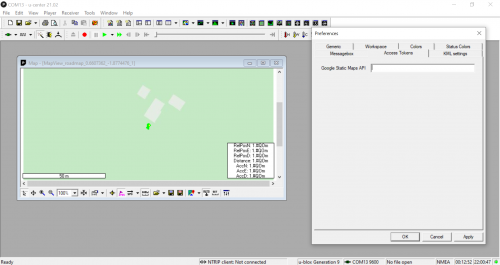
Google Maps Static API
There are multiple menus to utilize within u-center, one of which is the maps menu. By using Google Maps Static API, you can visualize the module spatially, as well as add speed vectors and scales. You'll need to add billing information to your Google Developer profile for the API to work properly.
There's also preferences for creating a Google Earth Server that will track in real time where your module is.
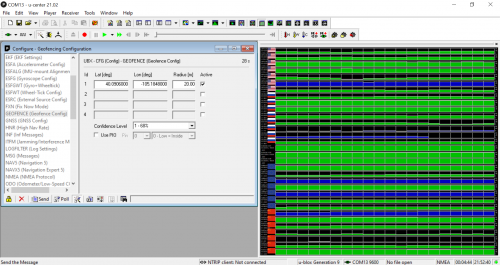
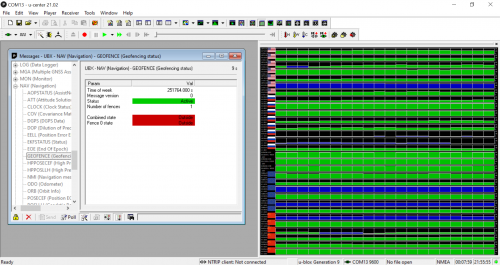
Setting up a Geofence
A key use case for a receiver as precise as this one is the ability to geofence, or create a boundary for the module's location. If the module leaves that boundary, then the user is notified that it has left that radius. U-center makes it easy to set this tool up. Within the configuration menu, you can set the latitude and longitude of the location, as well as radius that will serve as the boundary. Then, in the messages menu, under NAV, you'll be able to track whether the module is inside or outside of that radius you set up.
Learn more about u-center
U-center is a dense but extremely useful program for utilizing your GNSS receiver to it's full potential. There's tons more information not included in this blog, like logging data into a database, utilizing camera view, and so much more. If you're interested in these features, check out the in-depth user guide, or comment below on what parts of the software you'd like us to dig into to help you with your projects. In the meantime, put that brand new MicroMod GNSS Carrier Board to good use, and track where it is (and isn't) at all times. Happy Hacking!

Ready to get hands-on with GNSS?
We have a page just for you! We'll walk you through the basics of how GPS/GNSS works, the hardware needed, and project tutorials to get you started.