Python for SparkFun's Qwiic Connect System
A new package is available that incorporates all Qwiic modules capable of Python.
This information can also be found on our new Qwiic Py GitHub Repo. Make sure to head over there after reading about it!
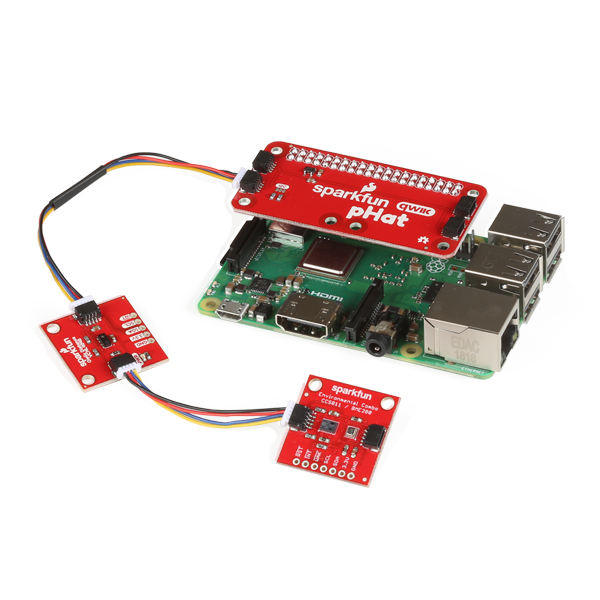
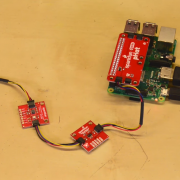
The SparkFun Qwiic Python package aggregates all Python Qwiic drivers/modules to provide a single entity for Qwiic within a Python environment. The Qwiic package delivers the high-level functionality needed to dynamically discover connected Qwiic devices and construct their associated driver object. That means that Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson Nano, and Google Coral can now, all implement the SparkFun Qwiic Connect System through Python!
Structure
Each Qwiic board has an independent driver library that implements the required logic for the specific board. This driver implementation is structured as a Python package that supports standard Python package management operations and tools. Additionally, each driver is deployed in a distinct GitHub repository, which provides a central area for package management and development.
To provide dynamic discovery and instantiation capabilities, the Qwiic package imports all the underlying Qwiic driver packages at runtime. As such, the Qwiic driver packages must be installed prior to using this package. These packages can be installed manually, or the overall package will install them automatically when using a "PyPi" based package manger (aka pip).
Dependent Modules
To make development and evaluation easier, the modules this package is dependent on are included in this repository as git submodules. This allows rapid checkout and access to the entire Qwiic Python ecosystem if needed.
This structure has the following layout:
Qwiic_Py/
+--- drivers/
| |--- qwiic_bme280 --> The qwiic_bme280 submodule
| |--- qwiic_micro_oled --> The qwiic_micro_oled submodule
| `--- ... links to qwiic driver submodule repositories
|
+--- qwiic_i2c/ --> Link to the qwiic_i2c submodule repository
| |--- __index__.py
| `--- ... The cross platform I2C bus access driver
|
+--- qwiic/
| |--- __index__.py
| `--- ... Package Implementation
|
+--- README.md
+--- setup.py
`--- ...etc
Dependencies
The Qwiic package depends on the Qwiic I2C driver: Qwiic_I2C_Py
This package is also dependent on the driver packages contained in the drivers directory.
Installation
PyPi Installation
This repository is hosted on PyPi as the "sparkfun-qwiic" package. On systems that support PyPi installation via pip, this package is installed using the following commands for all users (note: the user must have sudo privileges):
sudo pip install sparkfun-qwiic
For the current user:
pip install sparkfun-qwiic
This process will also install all modules the Qwiic package requires for operation, including the needed Qwiic driver packages.
Local Installation
To install, make sure the setuptools package is installed on the system.
Direct installation at the command line:
python setup.py install
To build a package for use with pip:
python setup.py sdist
A package file is built and placed in a subdirectory called dist. This package file can be installed using pip.
cd dist
pip install sparkfun_qwiic_-<version>.tar.gz
Example Use
import qwiic
results = qwiic.list_devices()
print(results)
>> [(61, 'Qwiic Micro OLED', 'QwiicMicroOled'), (91, 'Qwiic CCS811', 'QwiicCcs811'),
>> (96, 'Qwiic Proximity Sensor', 'QwiicProximity'), (119, 'Qwiic BME280', 'QwiicBme280')]
# Create a Micro OLED driver object using the I2C address of the board.
mydevice = qwiic.create_device(results[0][0])
print(mydevice)
>> <qwiic_micro_oled.qwiic_micro_oled.QwiicMicroOled object at 0x751fdab0>