SparkFun's New Product Process
In honor of Manufacturing Day 2014 (Friday, October 3rd) - We take a look at how SparkFun puts a dozen or so new products on the website each week.
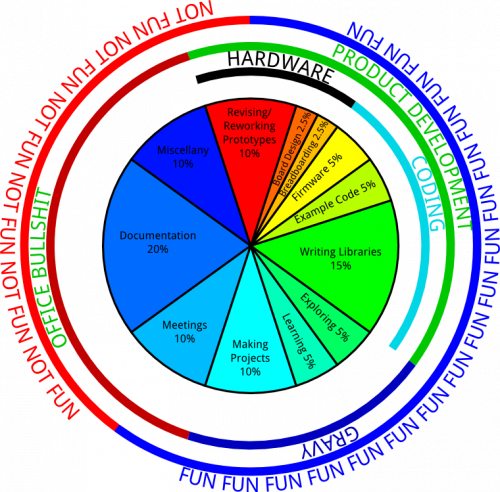
SparkFun was started with the goal to make it quick and easy for anyone to invent and prototype. Part of that goal depends on our ability to make and revise products continually to stay relevant to what the DIY electronics community is interested in, from the latest trends - like IoT and drones - to classic programming and electrical engineering. SparkFun has been consistently good at in-house production of simple, functional specialty boards and kits designed to give prototypers shortcuts; today, almost half our sales (44%) come from making and selling “SparkFun Originals.”
To coincide with Manufacturing Day 2014 (this year on Friday, October 3), I walked around the building to see if I could document how we put a dozen or so new products on the website every week. Many things contribute to that process, from Lunch & Learns to the early adoption of the beer license, but the engineering department unquestionably leads the charge.
A significant part of the engineering process is the weekly engineering meeting. Two hours every Monday morning are dedicated to pitching and evaluating new ideas. There is a lot of laughter heard through the walls, but there is at least a hint of seriousness to the meetings, since the group is vetting what will eventually be made by SparkFun.
DISCOVERY
Ideas are born everywhere - inside and outside our headquarters. Fifteen percent of the ideas for SparkFun Originals come from outside the building (which we then pay royalties on). But within the building, there is one staffer dedicated to fueling the new product pipeline.
One engineer’s input holds a bit more weight on the final cuts - Chris Taylor, Engineering’s project manager:
And some products come straight out of someone’s hobby, such as the SparkPunk.
Ideas that pass muster are put into our open source bug tracking software, which doubles as a project management tool. An engineer is assigned, if there isn’t one already, and priority is discussed - products that don’t already exist elsewhere are given precedence.
PROTOTYPING
After the discovery process, the engineers start prototyping. This is iterative and requires real paper and pencil and, well, engineering -revising reworking, board design, breadboarding, firmware, etc. Eventually a “green board” or prototype board is conceived (final boards are SparkFun red).
After a prototype is revised, it will be tested and then breadboarded. This requires a 3rd party - SparkFun uses OSHPark or Gold Phoenix for PCB assembly. The engineer then tweaks the schematic, creates a working circuit, finds the parts and creates a Bill of Materials.
Manufactured prototype boards then make another appearance at the Engineering meeting for review. Every Monday morning, there are two or three boards under review.
This is usually where Yak Shaving comes in.
The eventual result is open-sourced Eagle files, schematics, PCB files, design documents, hook up guides or kit cards, example code, libraries and GitHub repos.
The importance of this tool cannot be overstated.
“This is the kind of information that was helpful to me when I was a student (in Applied Math at CU Boulder),” _said Toni, _“so I Iike sharing it now. I also get to know what is going on with all of our products.”
We also test everything at SparkFun. Or at least we try.
Board assemblies, on the other hand, get a custom designed test jig. Pogo pins (aka bed-of-nails) are used – boards are pressed down on a jig designed to test all the solder joints. The jigs are designed to turn everything on, and a green LED lights up if all is well. If not, the techs fix errors manually. For more on this, see Constant Innovation in QC.
PRODUCTION
Parts are purchased for final boards, which are then built downstairs by hand in Production.
Figuring out how many boards to build for the initial run requires basic math. A buck panel is a unit of measure by Gold Phoenix that is $100 of square inches of circuit boards. We purchase 1, 2, or 3 buck panels. Once this is done, Inventory orders the panels and parts, and part numbers are put into the system.
After testing, a full run is scheduled and additional parts are purchased. This information feeds the schedule in production.
KITTING
At any give time, about 33 percent of SparkFun Originals are kits like the SparkPunk. What does it take to be a good kitter?
Each kitter works on 25-30 batches of kits over the span of a week, usually resulting in 4000 total kits per month.
On average it takes us 1.3 minutes to put together one kit. Some take 20 seconds and some take six to seven minutes. All of the kitters have side projects, and they all work on automating and optimizing the efficiency of their jobs. A lot of kitters end up advancing through the ranks at SparkFun; the group is open and communication is key.
LAUNCH
At this stage, engineering has left the product design spotlight. Engineers continue to receive email updates on every comment posted to one of their boards, and the keep an eye out for pitfalls customers are having and things they like. It is through this interaction with the community that the designs are improved.
“Writing the Hook Up Guides – especially for kits – is nontrivial,” said Byron.
The engineers also pass their hookup guides on to Jim or Joel for editing. Fritzing boards (visual renderings of how the board is hooked up) are created by Pamela Cortez to accompany the hook-up guides. This file also goes into GitHub.
The product is given a SKU, a description is written by Chris McCarty in Catalog, and a product page is built and given all the documentation links. Juan and Chelsea shoot and edit product photos, and Nick Poole, Robert Cowan, and Gregg Barclay prep for and shoot the New Product Friday video.